Hyperbole
Definition of hyperbole
There are many definition of hyperbole :
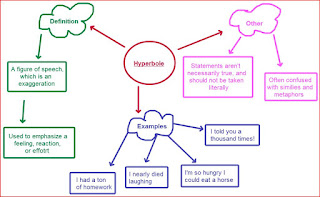
- · Hyperbole, derived from a Greek word meaning “over-casting” is a figure of speech, which involves an exaggeration of ideas for the sake of emphasis.
- · Hyperbole is a figure of speech that uses an exaggerated or extravagant statement to create a strong emotional response. As a figure of speech it is not intended to be taken literally. Hyperbole is frequently used for humour
- · A hyperbole is a literary device wherein the author uses specific words and phrases that exaggerate and overemphasize the basic crux of the statement in order to produce a grander, more noticeable effect.
Purpose of hyperbole
The purpose of hyperbole is
to create a larger-than-life effect and overly stress a specific point. Such
sentences usually convey an action or sentiment that is generally not practically/
realistically possible or plausible but helps emphasize an emotion.
It is a device that we employ in our day-to-day speech. For instance,
when you meet a friend after a long time, you say, “Ages have passed since I
last saw you”. You may not have met him for three or four hours or a day, but
the use of the word “ages” exaggerates this statement to add emphasis to your
wait. Therefore, a hyperbole is an unreal exaggeration to emphasize the
real situation
Hyperbole examples are given below.
- My grandmother is as old as the hills.
- Your suitcase weighs a ton!
- She is as heavy as an elephant!
- I am dying of shame.
It is important not to
confuse hyperbole with simile and metaphor. It does make a comparison
but unlike simile and metaphor, hyperbole has a humorous effect created by an overstatement
Examples from Classical English literature in
which hyperbole was used successfully.
From
William Shakespeare’s “Macbeth”,
Act II, Scene II,
“Neptune’s
ocean wash this blood
Clean from my hand? No. This my hand will rather
The multitudinous seas incarnadine,
Making the green one red.”
Clean from my hand? No. This my hand will rather
The multitudinous seas incarnadine,
Making the green one red.”
Macbeth,
the tragic hero,
feels the unbearable prick of his conscience after killing the king. He regrets
his sin and believes that even the oceans of the greatest magnitude cannot wash
the blood of the king off his hands. We can notice the effective use of
hyperboles in the given lines.
Function of Hyperbole
The
above arguments make clear the use of hyperbole. In our daily conversation, we
use hyperbole to emphasize for an amusing effect. However, in literature it has
very serious implications. By using hyperbole, a writer or a poet makes common
human feelings remarkable and intense to such an extent that they do not remain
ordinary. In literature, usage of hyperbole develops contrasts. When one thing
is described with an over-statement and the other thing is presented normally,
a striking contrast is developed. This technique is employed to catch the
reader’s attention
you can see in youtube
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperbole
http://www.myenglishpages.com/site_php_files/writing-hyperbole.php